摘要:在本教程中,您将学习如何使用 JavaScript 检查元素是否在视窗中可见。
当元素位于视窗中时,它会出现在屏幕的可见部分。
要检查元素是否在视窗中可见,您可以使用以下 isInViewport() 辅助函数
function isInViewport(element) {
const rect = element.getBoundingClientRect();
return (
rect.top >= 0 &&
rect.left >= 0 &&
rect.bottom <= (window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight) &&
rect.right <= (window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth)
);
}
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)如果元素在视窗中,该函数将返回 true。否则,它将返回 false。
检查元素是否在视窗中可见有很多应用,例如
- 执行延迟加载图像。只有当其容器在当前视窗中可见时,您才加载图像。这提高了页面的加载速度。
- 加载脚本以在视窗中显示广告。这为广告商节省了大量资金,避免了用户可能无法看到低于折叠广告的展示费用。
让我们深入了解 isInViewport() 函数,以了解它的工作原理。
获取元素的相对位置
方法 element.getBoundingClientRect() 提供元素的位置及其相对于视窗的相对位置。
它返回一个对象,其中包含元素的高度、宽度及其到视窗顶部、左侧、底部和右侧的距离。
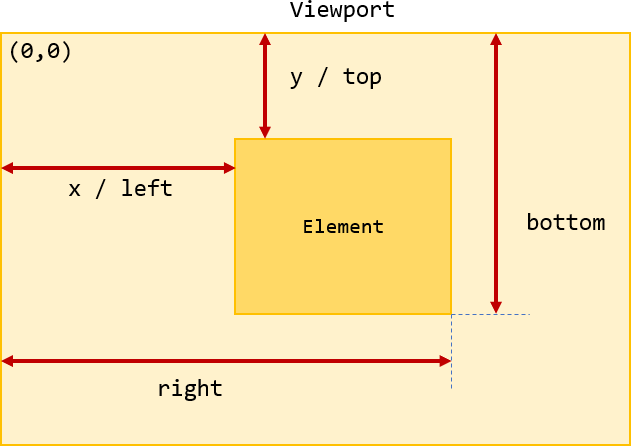
假设您有如下 <div> 元素
<div class="box"></div>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)要获取 <div> 元素在视窗中的位置,您可以使用 getBoundingClientRect() 方法
const box = document.querySelector('.box');
const rect = box.getBoundingClientRect();
console.log(rect);
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)输出
{
x: 100
y: 182
width: 300
height: 250
top: 182
right: 400
bottom: 432
left: 100
}
Code language: CSS (css)如果 <div> 元素在视窗中,它的顶部和左侧始终大于或等于零。此外,它到右侧的距离小于或等于视窗的宽度,它到底部的距离小于或等于视窗的高度。
要获取视窗的宽度和高度,您可以使用现代浏览器中的 window.innerWidth 和 window.innerHeight。但是,某些浏览器使用 document.documentElement.clientWidth 和 document.documentElement.clientHeight。
要支持所有浏览器,您可以尝试一个并回退到另一个,如下所示
const viewportWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth;
const viewportHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight;Code language: JavaScript (javascript)以下检测 <div> 元素是否在视窗中
const box = document.querySelector('.box');
const rect = box.getBoundingClientRect();
const isInViewport = rect.top >= 0 &&
rect.left >= 0 &&
rect.bottom <= (window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight) &&
rect.right <= (window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth);
console.log(isInViewport);Code language: JavaScript (javascript)因此,您可以将逻辑包装在辅助函数 isInViewport() 中,并按如下方式使用它
const box = document.querySelector('.box');
const result = isInViewport(box);Code language: JavaScript (javascript)当您滚动文档时,该框将不再在视窗中。要监控这一点,您可以 监听滚动事件 并将结果显示在另一个 div 元素中。
以下是 HTML 页面
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Check if an element is visible in the viewport</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style-viewport.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"></div>
<div id="message">Please scroll to check if the box is visible</div>
<script src="js/app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)以下是 JavaScript 文件
function isInViewport(el) {
const rect = el.getBoundingClientRect();
return (
rect.top >= 0 &&
rect.left >= 0 &&
rect.bottom <= (window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight) &&
rect.right <= (window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth)
);
}
const box = document.querySelector('.box');
const message = document.querySelector('#message');
document.addEventListener('scroll', function () {
const messageText = isInViewport(box) ?
'The box is visible in the viewport' :
'The box is not visible in the viewport';
message.textContent = messageText;
}, {
passive: true
});
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)输出
总结
- 使用
getBoundingClientRect()方法获取元素的大小及其相对于视窗的相对位置。 - 将元素的位置与视窗的高度和宽度进行比较,以检查元素是否在视窗中可见。